APM Forests - A Glimpse of the 90s
R McCarthy
Overview & Planning
Overview
APM Forests (APMF) was formed in 1951 by Australian Paper Manufacturers (APM) (which became a wholly-owned subsidiary of AMCOR Ltd) with the primary aim of supplying economic pulpwood to APM's Maryvale Mill in Gippsland, through the establishment of a plantation base and co-ordination of pulpwood harvesting. APMF operations included:
- Growing, harvesting and transportation of APMF plantation-grown pine and eucalypt to the Maryvale Mill.
- Negotiating wood prices and supervising the supply of wood and wood chips from the State Government and private suppliers.
- Growing, harvesting and transportation of APMF plantation-grown sawlogs to the APM Wood Products Sawmill at Morwell.
- Sales of logs and seedlings to external customers.
- Establishment and maintenance of plantations.
- Research and development in tree breeding and tree growth.
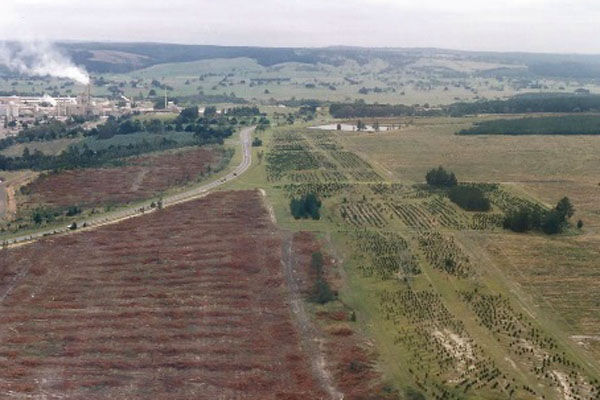
By 2001, the APMF gross land holding (including freehold and leasehold land) in Gippsland was 85,000ha. Of this land base:
- The net productive plantation area was 62,500ha, comprising 42,500ha of pine plantations, 7000ha of eucalypt plantations, 7000ha of eucalypt native forest and 6000ha of plantation land awaiting replanting (following plantation clear-falling).
- The non-productive land base of some 22,500ha across the estate comprised land occupied by roads, firebreaks, riparian strips, swamps, mineral resources, housing areas and power transmission lines etc.
- The annual planting rate averaged 1500 to 2000ha/yr.
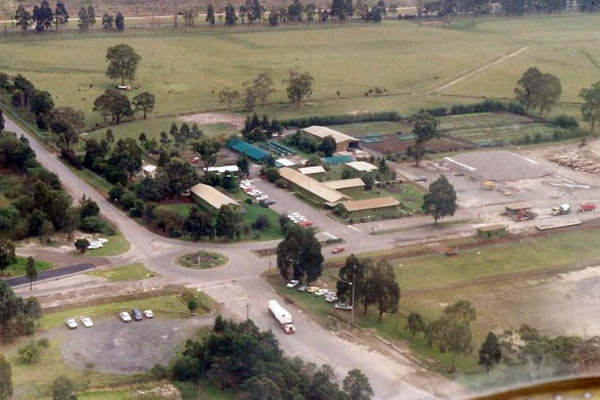

APMF office and nursery
1993
Photo: R McCarthy
By 2001, the volume of wood harvested annually both from APMF plantations and State Forests was approximately 1.4 million tonnes. In that year the plantations were sold to Hancock Victorian Plantations (HVP).
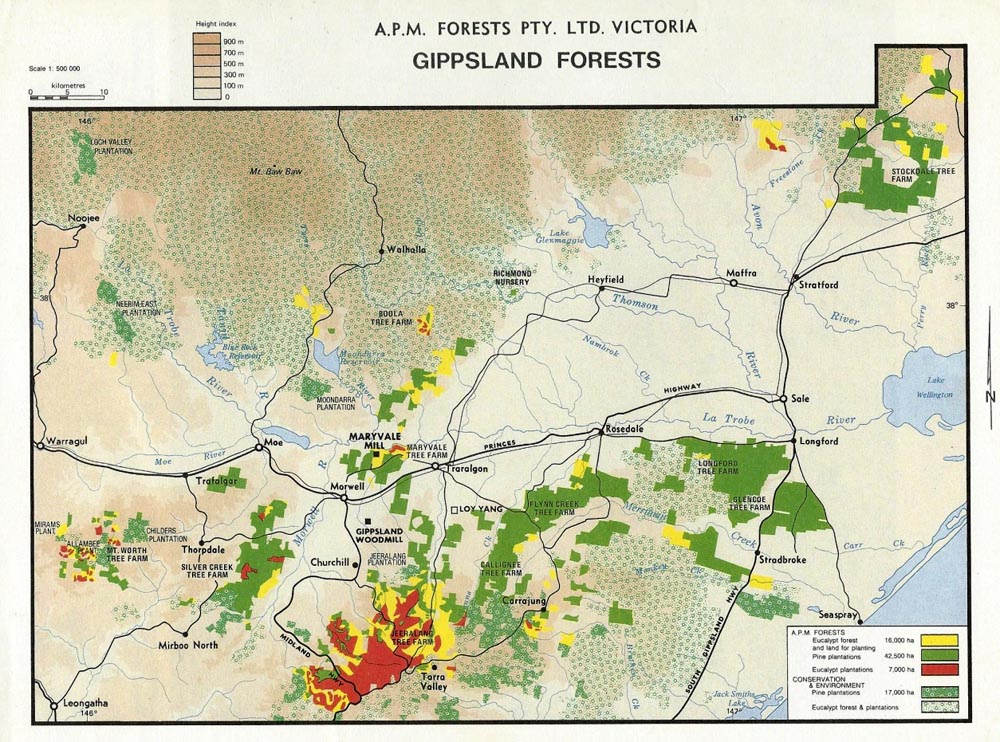
APMF land holdings Gippsland 1990
Planning
To plan plantation and industrial development within Gippsland, APMF constructed a long-term plantation planning model using simulation and linear programming techniques. This model undertook explicit evaluation of the combination and interactions of establishment method, tree breeding, fertilisation, thinning type and clear-felling age.
APMF's geographic information system incorporated the results of an extensive soil survey and associated mapping exercise across the whole estate. For each site this defined prescriptive treatments for soil cultivation, nutritional requirements and use of weedicide. An example is given in Table 1 of this work in relation to P. radiata.
Management Regimes
Pine Plantations
APM Forests commenced thinning its 12-year-old pine plantations in 1962. The total annual pine wood input to Maryvale Mill was approximately 50,000m3 being supplied mainly from State plantations at a considerable distance from the mill. Input doubled the next year and redoubled in 1970. However, this young wood from the company plantations was not particularly attractive to Maryvale. The discovery of Sirex made the large-scale thinning of the plantations an urgent matter. As an outlet for this young wood a particle board factory was established at Rosedale, jointly owned by CSR and APM Forests. Production commenced in 1964 and wood intake increased to 50,000m3 per year. Because of its small size the factory became unprofitable and was closed at the end of 1978. Later, biological control of Sirex was developed.
During this period, the plantations were intensively managed with thinning commencing at age 10/11 and repeated at 2- to 3-year intervals. Demand was in excess of supply necessitating the purchase of wood from external sources at high cost. This intensive thinning minimised losses from Sirex attack in this period prior to biological control. Wood from second and subsequent thinnings from age 14 on was suitable for pulp mill requirements.
Although the plantations were planned to be pulpwood only, by the mid 1970s when the oldest plantings were 25 years old, the suitability of the pine resource for sawn timber production was investigated. The outcome was the establishment of a large sawmill at Morwell. Log intake commenced in 1976 with that from the company plantations increasing from an initial level of 50,000m3 to 100,000m3 in 1988 with further increases thereafter.
A major new pine Kraft pulp mill on the existing Maryvale site was planned for commencement around 1978. The minimum economic size for such a mill was then considered to be approximately 150,000 tonnes of pulp per year. To meet this project demand, planting rates were increased considerably in 1973. The new mill eventually commenced operation in 1985 with a capacity of 160,000 tonnes of pulp per year.
In the 1990s output from the plantations was 650-700,000m3/yr of pulpwood, sawlogs and peeler logs for external sales.
Planting rates averaged 1300ha/yr with clear-felling averaging 1000ha/yr.
By the 1990s growth was in excess of pulpwood demand. A less intensive silvicultural regime evolved with three thinnings. (First thinning at age 14-15 years with subsequent thinnings at 4 year intervals and clear-felling at age 26 to 28 years.)
Eucalypt Plantations
Some native forests were purchased from the start of APMF operations including some natural regeneration on partially cleared farmland. Various thinning, timber stand improvement and other treatments were applied in the 1950s and 1960s but results were generally disappointing in terms of wood production.
Small trial plantings of several species of eucalypts commenced from 1952, but remained on a small scale until the commencement of the Strzelecki Project (Heartbreak Hills) for the future supply of additional eucalypt pulpwood in 1960. Successful establishment on this very steep topography was not readily achievable until the control of browsing animals was available through the introduction of myxomatosis and the use of 1080 poisoning.
Plantings were mainly of E. regnans with some E. globulus. In the 1960s plantings averaged about 200ha/yr and in the 1970s approximately 500ha/yr until the leasehold areas were completed. Then, because of increased availability of residual roundwood from State Forests, in the next seven years a total of only 370ha were planted.
In the early 1980s, APM decided to expand significantly into the business papers segment of the paper market, requiring a major rebuild of a paper machine and expansion of bleached eucalypt pulp output, requiring an increasing input of eucalypt wood.
The eucalypt plantation program was reactivated in 1986. Planting rates commenced at 100ha/yr rising to 800ha/yr in 1989. It was envisaged that the rotation age for E. regnans plantations would be about 30 years. For other eucalypt species shorter rotation ages were envisaged.
Plantation eucalypt research was greatly expanded with the establishment of a eucalypt seed orchard, eucalypt harvesting thinning operations in both plantation and natural regeneration areas and a comprehensive program of wood and pulping quality investigations.

Jeeralang Tree Farm - E.regnans planted in 1961
1991
Photo: R McCarthy

Jeeralang Tree Farm - E.regnans planted in 1961
1991
Photo: R McCarthy
Land Capability Criteria
In assessing areas for plantation development, the following criteria applied:
- Rainfall should not be less than 800mm/yr.
- Within 100km of a processing plant and preferably within 50km.
- Preferably with slopes of less than 12 degrees and no more than 20 degrees.
- Individual blocks should be 100ha and reasonably compact in shape.
- At least 16m3/ha/yr MAI at age 20.
- Soils to exhibit load carrying capacity in winter.
- Year-round access for extraction of forest produce.
- Appropriate for perpetual forestry activities.
- Free of noxious weeds/pests and diseases.
- Access to inexpensive roading materials.
- Size and vegetation cover such that the new plantation crop could be economically protected from fire.
- Reasonably well drained.
Plantation Layout
Size
Each compartment of the plantation estate was approximately 40ha, but this varied according to plantable area and geographic features.
Buffer Zones
Water courses and depressions were protected by a buffer zone of undisturbed vegetation. For minor depressions which drain short and gentle slopes, a total buffer of 20m was generally adequate. On well-defined water courses, a minimum buffer of 20m was allowed. Earthworks and vehicular activity were excluded from the buffer zones.
Roads
As far as practicable roads were located adjacent to each compartment of planted trees.
All internal access roads were trafficable throughout the fire season. In hilly country, internal ridge tracks (to a maximum grade of 1 in 10) were maintained.
The main road network was trafficable to all vehicles and maintained in this state by appropriate methods such as grading and slashing.
No roads were allowed to dead-end for reasons of fire safety.
Firebreaks
- External firebreaks of 7-20m width were established on the upwind boundaries (usually on the northern, southern and western boundaries) of the block, where the land was accessible by machine. A vehicular track was placed on these firebreaks where practicable.
- Firebreaks were maintained in a vegetation-free condition by appropriate methods such as disc ploughing (to prevent erosion), grading, grazing and tractor slashing.
- In hilly country, where mechanical cultivation of firebreaks was not possible, the external boundaries were manually cleared of vegetation, as necessary.
- There was an all-weather track within 400m of any point of the plantation.
- All tracks were negotiable by a four-wheel-drive fire tanker in summer conditions.
- If a track became impassable to a four-wheel-drive tanker it was signposted as such at the nearest track junction at which the fire tanker could turn.
- Wherever possible, dead end tracks were avoided on firebreaks
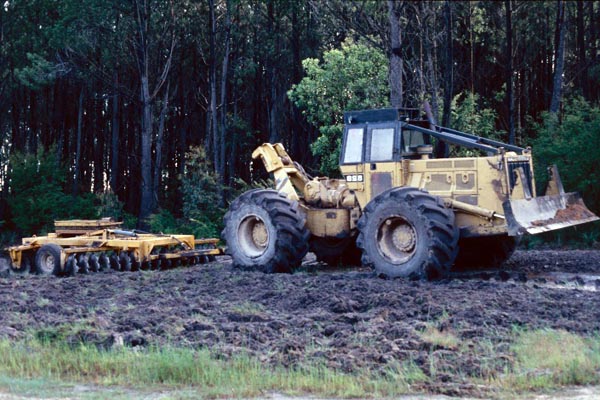

Cat 528 skidder with disc plough on firebreaks
1993
Photo: R McCarthy
Water Supply
- Where the soils would hold water, fire dams were established for each 100ha of plantation.
- Fire dams were greater than 100,000 litres capacity.
- Fire dams were to be accessible by helicopter and fire tanker and to be located alongside all-weather roads.
- Maximum distance to any water point was no more than 2km.
Plantation Establishment
Site Preparation
Chopper Rolling
For second rotation sites, there was no burning of slash from previous harvests. All slash was macerated by chopper-rolling to ensure it was incorporated back into the site to reduce loss of organic matter and nutrients.
Cultivation
All plantation sites were cultivated prior to planting.Moderate Topography
Depending on the soil type, cultivation was by one of three methods:- For moderate topography with sandy and sandy-loam soils, each planting line was cultivated and mounded (using a Savannah stump-jump plough pulled by a large rubber-tyred skidder) at one to two degrees off the contour at three-metre intervals. In laying out the pattern of cultivation, each segment of the area was considered in isolation for drainage aspects and prevention of erosion. All rows were to be accessible to a firebreak or road for extraction of forest produce.
- On steeper topography or hard-pan areas or heavy clay-loam soils, soils were ripped with a winged ripper to one metre depth and the topsoils cultivated with a twin set of discs mounted on the ripper to create a mound. A cultivator could be used on grassed sites to break the large clods resulting from the ripping operation. Ripping was done using a D7-sized bulldozer on the contour at three-metre intervals.
Planting
On undulating topography free of remnant vegetation, mechanical planting machines were used for P. radiata seedlings. On second rotation sites with undulating topography, hand planting was undertaken. Where mechanical cultivation was not possible, such as on steep topography, hand cultivation of the planting site was undertaken prior to planting.
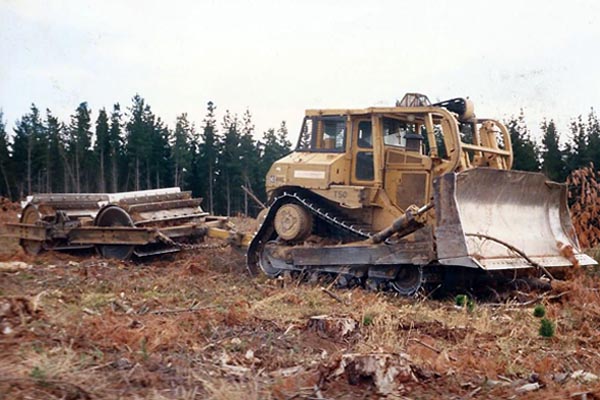

Preparing 2nd rotation site - Twin Marden chopper-rollers pulled by Cat D8
1992
Photo: R McCarthy
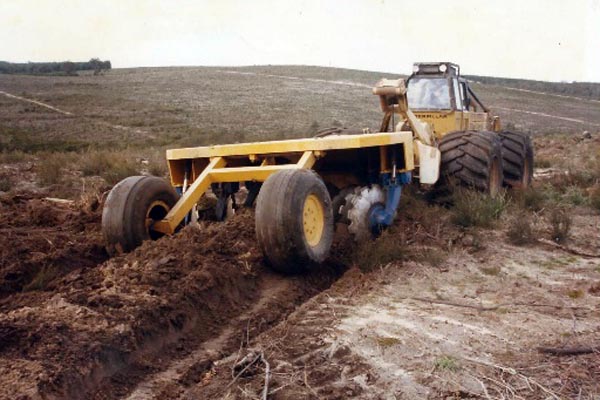

Savannah stump-jump mounding plough pulled by Cat 528 Skidder
1991
Photo: R McCarthy
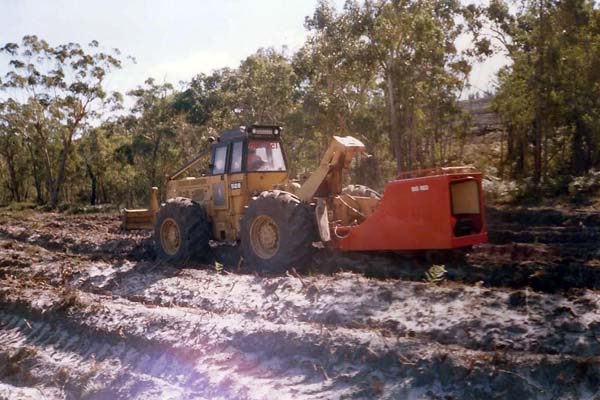

Machine planting - Longford Tree Farm
1989
Photo: R McCarthy
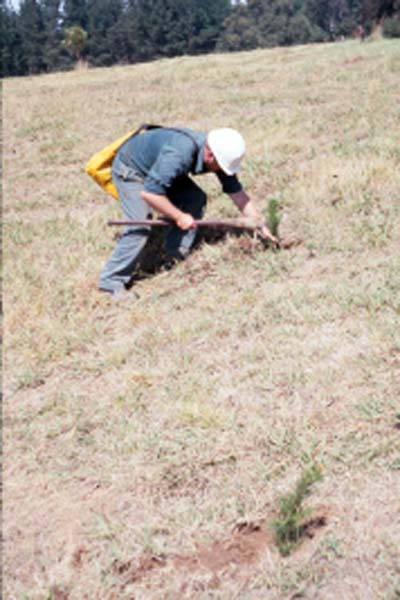

Hand planting a steep uncultivated area
1992
Photo: R McCarthy
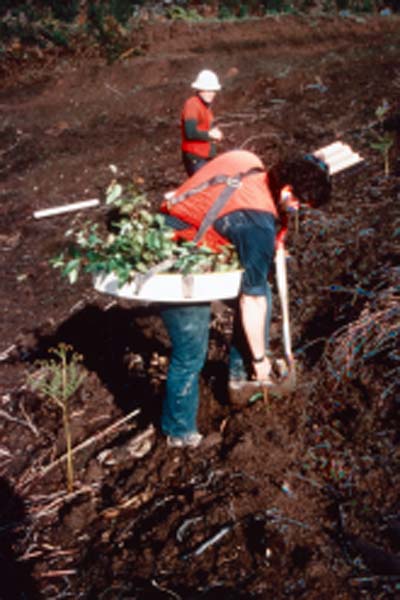

Hand planting - containerised eucalypt seedlings
1992
Photo: R McCarthy
Environment & Safety
APMF placed environmental and safety considerations high on its management agenda. Operations were undertaken in conformance with Victoria's Code of Forest Practices for Timber Production. Professional forest scientists were employed to ensure that soil, hydrology, flora and fauna, aesthetic values, diseases and weed problems were considered in plantation operations.
For example:- Since 1978, soil cultivation was carried out on the contour leaving a double furrow surrounding undisturbed soil between each ridge.
- APMF recognised early the importance of avoiding windrowing and burning of slash on second rotation sites to avoid second rotation decline. APMF quickly developed appropriate slash incorporation techniques using chopper rolling and stump-jump ploughs that retain and incorporate organic matter and nutrients in the logging slash.
Utilisation of Areas Unable to Carry Plantation
Christmas tree plantations were established beneath major electricity transmission lines.
Weed Control
APMF was one of the first forestry organisations to voluntarily cease using 245-T and 24-D and stop the application of herbicides from the air. In 1981 APMF introduced goats for the biological control of blackberries and other noxious weeds in its plantations. The project was described by the author in 1985.
Control of Feral Animals
APMF responded to public concern over the use of 1080 and mounted a substantial research program with the objective of finding acceptable alternatives for avoiding browsing damage in young plantations.
Farm Forestry Agreement
To offer landholders in Gippsland an incentive to invest in tree farming, the Farm Forestry Agreement was initiated in 1975. This scheme was complementary to the former FCV Farm Forestry Loan scheme.
School Plantations
APMF operated a school plantation scheme in Central Gippsland for over 40 years. Schools were leased an area of one hectare. APMF was responsible for planting and maintaining the plantation. The school received all royalties from the plantation at the time of harvest.

Christmas trees under transmission lines
1993
Photo: R McCarthy

Mechanised weed control using a Cat 528 skidder
1992
Photo: R McCarthy

Pre-emergent weed control - eucalypt establishment area
1993
Photo: R McCarthy
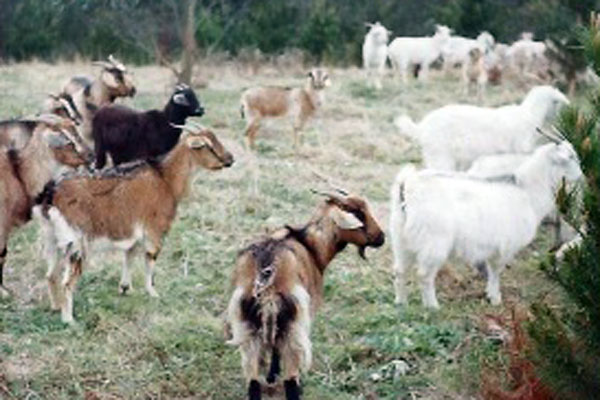

Goats being introduced to the Jeeralang Tree Farm
1981
Photo: R McCarthy

Before goats - Blackberry infestation, Jeeralang Tree Farm.
1988
Photo: R McCarthy

After 70 goats grazing for one month (see photo above), Jeeralang Tree Farm.
1988
Photo: R McCarthy
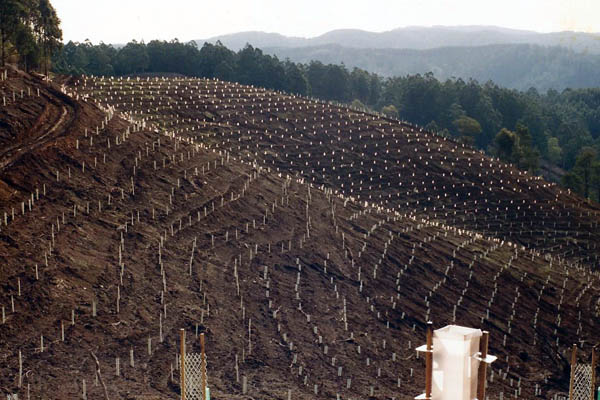

Protection from feral animals. Tree guards used with E. regnans planting, Jeeralang Tree Farm.
1992
Photo: R McCarthy
Strzelecki Project
See also: The Strzelecki Project
“APM Forests had a similar pattern of land acquisition and planting but without the help of prison labour. The company’s first plantings of pine and ash took place in 1960. The first purchases of land were made in the 1950’s and they have built up over the years until today they total about 24,000 hectares of freehold and 8617 hectares of leasehold. The leasehold land is held from the state under certain conditions regulating the way it is used for plantations. The total area of freehold and leasehold as of 1986 was 5030 hectares of pines and 4502 of eucalypts.
The conditions governing the lease of land by APM Forests provide that planting of the area must be completed within 15 years of the issue of the lease, which runs for 60 years. During that time, the company may use any timber it grows but must re-establish the plantations within three years of harvesting. The company pays an annual rent calculated at five percent of the unimproved valuation and is required to hand back in a reforested condition the area at the completion of the lease.”
